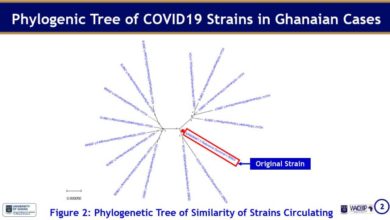
Hydroxychloroquin – Azithromycin: safe and efficient treatment for Covid19
Professor Didier Raoult Releases the Results of a New Hydroxychloroquine Treatment Study on 1061 Patients

A new study by performed at IHU Méditerranée Infection, Marseille, France has found Hydroxychloroquine–Azithromycin (HCQ-AZ) combination to be a safe and effective treatment for Covid19 when started immediately after diagnosis.
The study with a cohort of 1061 COVID-19 patients, treated for at least 3 days with the HCQ-AZ combination and a follow-up of at least 9 days was investigated established two key findings;
- No cardiac toxicity was observed.
- A good clinical outcome and virological cure was obtained in 973 patients within 10 days (91.7%).
However, a poor outcome was observed for 46 patients (4.3%); 10 were transferred to intensive care units, 5 patients died (0.47%) (74-95 years old) and 31 required 10 days of hospitalization or more.
The authors conclude that: “The HCQ-AZ combination, when started immediately after diagnosis, is a safe and efficient treatment for COVID-19, with a mortality rate of 0.5%, in elderly patients. It avoids worsening and clears virus persistence and contagiosity in most cases.”
See the complete abstract below.
Background
In a recent survey, most physicians worldwide considered that hydroxychloroquine (HCQ)
and azithromycin (AZ) are the two most effective drugs among available molecules against
COVID-19. Nevertheless, to date, one preliminary clinical trial only has demonstrated its
efficacy on the viral load. Additionally, a clinical study including 80 patients was published,
and in vitro efficiency of this association was demonstrated.
Methods
The study was performed at IHU Méditerranée Infection, Marseille, France. A cohort of 1061
COVID-19 patients, treated for at least 3 days with the HCQ-AZ combination and a follow-up
of at least 9 days was investigated. Endpoints were death, worsening and viral shedding
persistence.
Findings
From March 3rd to April 9th, 2020, 59,655 specimens from 38,617 patients were tested for
COVID-19 by PCR. Of the 3,165 positive patients placed in the care of our institute, 1061
previously unpublished patients met our inclusion criteria. Their mean age was 43.6 years old
and 492 were male (46.4%). No cardiac toxicity was observed. A good clinical outcome and
virological cure was obtained in 973 patients within 10 days (91.7%). Prolonged viral carriage
at completion of treatment was observed in 47 patients (4.4%) and was associated to a higher
viral load at diagnosis (p < 10-2) but viral culture was negative at day 10 and all but one were
PCR-cleared at day 15. A poor outcome was observed for 46 patients (4.3%); 10 were
transferred to intensive care units, 5 patients died (0.47%) (74-95 years old) and 31 required
10 days of hospitalization or more. Among this group, 25 patients are now cured and 16 are
still hospitalized (98% of patients cured so far). Poor clinical outcome was significantly
associated to older age (OR 1.11), initial higher severity (OR 10.05) and low 2
hydroxychloroquine serum concentration. In addition, both poor clinical and virological
outcomes were associated to the use of selective beta-blocking agents and angiotensin II
receptor blockers (P<0.05). Mortality was significantly lower in patients who had received >
3 days of HCQ-AZ than in patients treated with other regimens both at IHU and in all
Marseille public hospitals (p< 10-2).
Interpretation
The HCQ-AZ combination, when started immediately after diagnosis, is a safe and efficient
treatment for COVID-19, with a mortality rate of 0.5%, in elderly patients. It avoids
worsening and clears virus persistence and contagiosity in most cases.
The original abstract can be accessed here.
Also, the researchers made this table available.
Discover more from MedCircles Ghana
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.